Anti-EDA Antibody (CAB2905)
- SKU:
- CAB2905
- Product type:
- Antibody
- Reactivity:
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Host Species:
- Rabbit
- Isotype:
- IgG
- Research Area:
- Developmental Biology
Description
| Antibody Name: | Anti-EDA Antibody |
| Antibody SKU: | CAB2905 |
| Antibody Size: | 20uL, 50uL, 100uL |
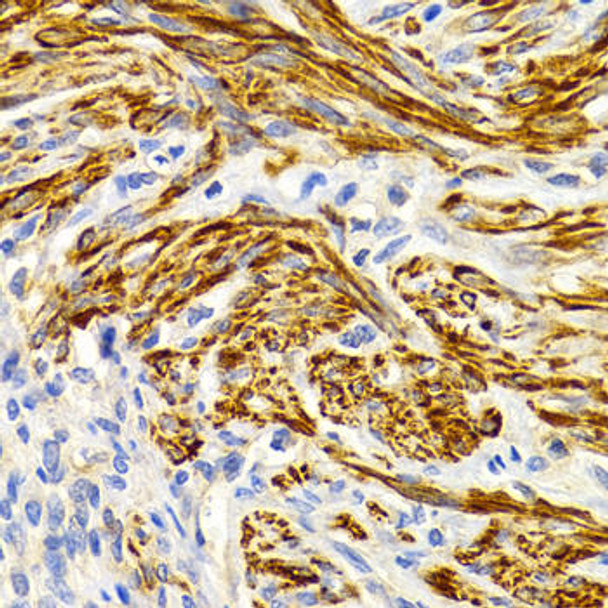
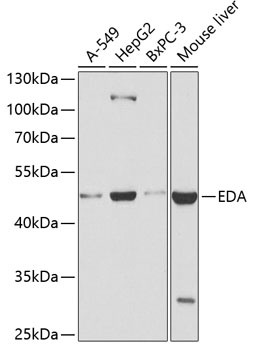
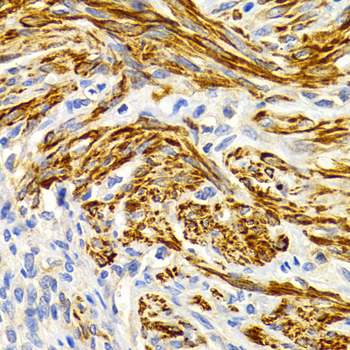
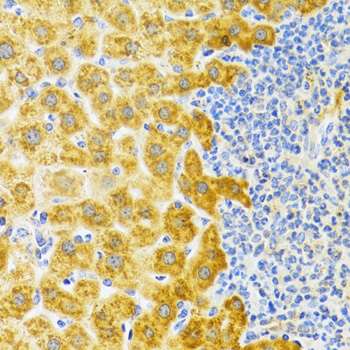
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host Species: | Rabbit |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human EDA |
| Application: | WB IHC |
| Recommended Dilution: | WB 1:500 - 1:2000 IHC 1:50 - 1:200 |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Positive Samples: | A-549, HepG2, BxPC-3, Mouse liver |
| Immunogen: | A synthetic peptide of human EDA |
| Purification Method: | Affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer: | Store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. Buffer: PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Sequence: | Email for sequence |
| Gene ID: | 1896 |
| Uniprot: | Q92838 |
| Cellular Location: | Cell membrane, Secreted, Single-pass type II membrane protein |
| Calculated MW: | 14kDa/15kDa/40kDa/41kDa |
| Observed MW: | 48kDa |
| Synonyms: | EDA, ECTD1, ED1, ED1-A1, ED1-A2, EDA-A1, EDA-A2, EDA1, EDA2, HED, HED1, ODT1, STHAGX1, TNLG7C, XHED, XLHED |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a type II membrane protein that can be cleaved by furin to produce a secreted form. The encoded protein, which belongs to the tumor necrosis factor family, acts as a homotrimer and may be involved in cell-cell signaling during the development of ectodermal organs. Defects in this gene are a cause of ectodermal dysplasia, anhidrotic, which is also known as X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Several transcript variants encoding many different isoforms have been found for this gene. |
| UniProt Protein Function: | EDA: Seems to be involved in epithelial-mesenchymal signaling during morphogenesis of ectodermal organs. Isoform 1 binds only to the receptor EDAR, while isoform 3 binds exclusively to the receptor XEDAR. Defects in EDA are the cause of ectodermal dysplasia type 1 (ED1); also known as Christ-Siemens-Touraine syndrome or X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (XLHED). Ectodermal dysplasia defines a heterogeneous group of disorders due to abnormal development of two or more ectodermal structures. ED1 is a disease characterized by sparse hair (atrichosis or hypotrichosis), abnormal or missing teeth and the inability to sweat due to the absence of sweat glands. ED1 is the most common form of over 150 clinically distinct ectodermal dysplasias. Defects in EDA are the cause of tooth agenesis selective X-linked type 1 (STHAGX1). A form of selective tooth agenesis, a common anomaly characterized by the congenital absence of one or more teeth. Selective tooth agenesis without associated systemic disorders has sometimes been divided into 2 types: oligodontia, defined as agenesis of 6 or more permanent teeth, and hypodontia, defined as agenesis of less than 6 teeth. The number in both cases does not include absence of third molars (wisdom teeth). Belongs to the tumor necrosis factor family. 8 isoforms of the human protein are produced by alternative splicing. |
| UniProt Protein Details: | Protein type:Receptor, misc.; Motility/polarity/chemotaxis; Membrane protein, integral Chromosomal Location of Human Ortholog: Xq12-q13.1 Cellular Component: endoplasmic reticulum membrane; collagen; cytoskeleton; membrane; intracellular membrane-bound organelle; apical part of cell; integral to plasma membrane; integral to membrane; plasma membrane; extracellular region Molecular Function:protein binding; tumor necrosis factor receptor binding; receptor binding Biological Process: pigmentation; cell-matrix adhesion; ectoderm development; immune response; positive regulation of NF-kappaB import into nucleus; gene expression; cell differentiation; signal transduction; activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor; odontogenesis of dentine-containing teeth Disease: Tooth Agenesis, Selective, X-linked, 1; Ectodermal Dysplasia 1, Hypohidrotic, X-linked |
| NCBI Summary: | The protein encoded by this gene is a type II membrane protein that can be cleaved by furin to produce a secreted form. The encoded protein, which belongs to the tumor necrosis factor family, acts as a homotrimer and may be involved in cell-cell signaling during the development of ectodermal organs. Defects in this gene are a cause of ectodermal dysplasia, anhidrotic, which is also known as X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Several transcript variants encoding many different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| UniProt Code: | Q92838 |
| NCBI GenInfo Identifier: | 6166135 |
| NCBI Gene ID: | 1896 |
| NCBI Accession: | Q92838.2 |
| UniProt Secondary Accession: | Q92838,O75910, Q5JS00, Q5JUM7, Q9UP77, Q9Y6L0, Q9Y6L1 Q9Y6L2, A0AUZ2, A2A337, B7ZLU2, B7ZLU4, |
| UniProt Related Accession: | Q92838 |
| Molecular Weight: | 40,750 Da |
| NCBI Full Name: | Ectodysplasin-A |
| NCBI Synonym Full Names: | ectodysplasin A |
| NCBI Official Symbol: | EDA |
| NCBI Official Synonym Symbols: | ED1; HED; EDA1; EDA2; HED1; ODT1; XHED; ECTD1; XLHED; ED1-A1; ED1-A2; EDA-A1; EDA-A2; STHAGX1 |
| NCBI Protein Information: | ectodysplasin-A; oligodontia 1; X-linked anhidroitic ectodermal dysplasia protein |
| UniProt Protein Name: | Ectodysplasin-A |
| UniProt Synonym Protein Names: | Ectodermal dysplasia protein; EDA protein |
| Protein Family: | Ectodysplasin |
| UniProt Gene Name: | EDA |
| UniProt Entry Name: | EDA_HUMAN |